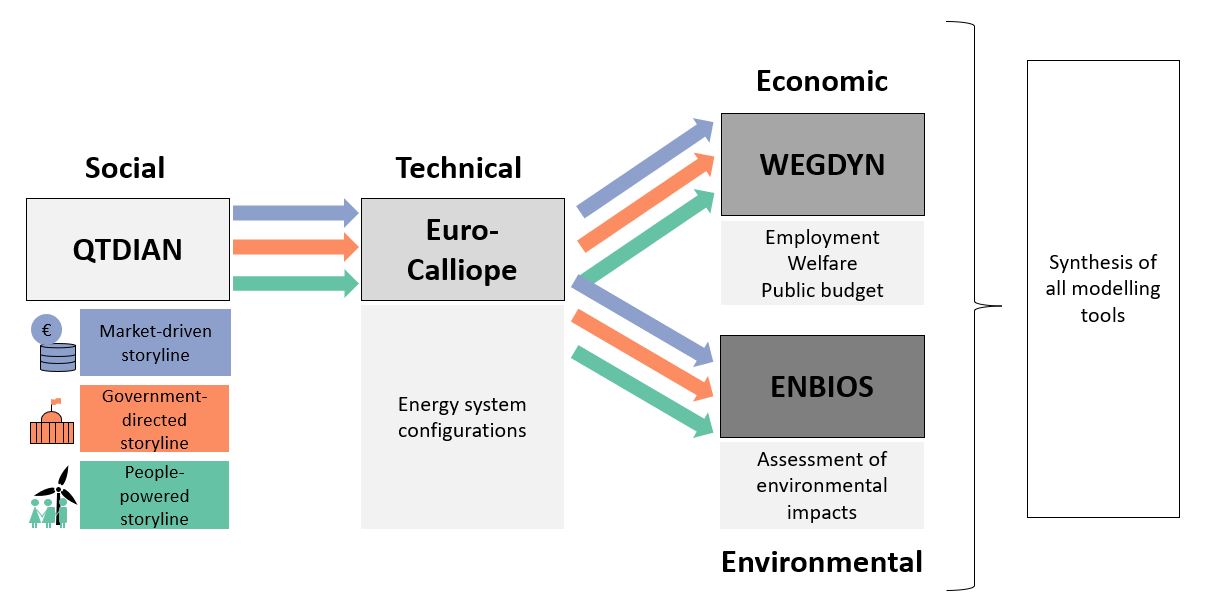
Energy models are used to inform and support decisions for the transition to climate neutrality. In recent years, such models have been criticised for being overly technology-centred and largely ignoring social and political developments and dynamics of the energy transition, such as preferences and acceptance of citizens and decision-makers. To help make models more realistic and policy-relevant, we developed QTDIAN (Quantification of socio-Technological DIffusion and sociAl constraiNts) − a toolbox of empirically-based qualitative and quantitative descriptions and boundary conditions of socio-technical and political aspects of the energy transition. We have linked QTDIAN with the energy demand models DESSTINEE, HEB and DREEM, the energy system model Euro-Calliope and indirectly with the economic equilibrium model WEGDYN and the environmental assessment model ENBIOS.
Papers:
Süsser, D., al Rakouki, H., & Lilliestam, J. (2021). The QTDIAN modelling toolbox–Quantification of social drivers and constraints of the diffusion of energy technologies. Deliverable 2.3. Sustainable Energy Transitions Laboratory (SENTINEL) project. Potsdam: Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies (IASS).
Süsser, D., Pickering, B., Chatterjee, S., Oreggioni, G., Stavrakas, V., & Lilliestam, J. (2021). Integration of socio-technological transition constraints into energy demand and systems models. Deliverable 2.5. Sustainable Energy Transitions Laboratory (SENTINEL) project. Potsdam: Institute for Advanced Sustainability Studies (IASS).
Süsser, D., Martin, N., Stavrakas, V., Gaschnig, H., Talens-Peiró, L., Flamos, A., Madrid-López, C., & Lilliestam, J. (2022). Why energy models should integrate social and environmental factors: Assessing user needs, omission impacts, and real-word accuracy in the European Union. Energy research & social science, 92: 102775. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.erss.2022.102775
Models used
QTDIAN
Euro-Calliope
WEGDYN
Computable general equilibrium model
DetailsDREEM
Dynamic, object-oriented, and equation-based high-resolution simulation model
DetailsDESSTINEE Supply
HEB
Building energy demand and CO2 emissions model
DetailsSENTINEL case study
Case study: Continental – Europe
Europe-wide opportunities and trade-offs with particular reflection on the concerns, needs and demands of stakeholders.
Details